Powershell-With-Sql
Here we will try to understand how powershell is usefull in to automate SQL activities such as backups and automate deployment.
BACKUP DATABASE Transact-SQL command has been around a long time,
Because If you are not doing backups, and ensuring that you can recover databases from those backups,
you are exposing yourself and your company to data loss.
There are multiple ways to automate SQL backups.
1. Manually schedule backups for each database as it is added.
2. After you install the instance run a script to generate backup jobs for each database.
Then periodically scan for new databases/databases not backed up and add backup jobs.
3. Schedule one backup job per instance to backup all local databases.
4. Use a central scheduling system
In SQL Server 2012, Microsoft added four new cmdlets for Backup and Restore:
Backup-SqlDatabase
Restore-SqlDatabase
Backup-ASDatabase
Restore-ASDatabase
If these commands are then question would arias in your mind why do we need to write scripting backups from an external process?
As number database increases and the backup process becomes more complex, more and more file-system work needs to be done. Scheduled jobs might need1. Naming convensions and
2. Arranging of backups into directories
3. Periodically deleting old backups those are no longer required
4. Checking backup integrity
5. Writing to logs and many more
6. Moving/Copying them some safelocation
When you start up PowerShell and want to work with the SQLPS module,
you need to use the Import-Module cmdlet.
PS C:> Import-module SQLPS
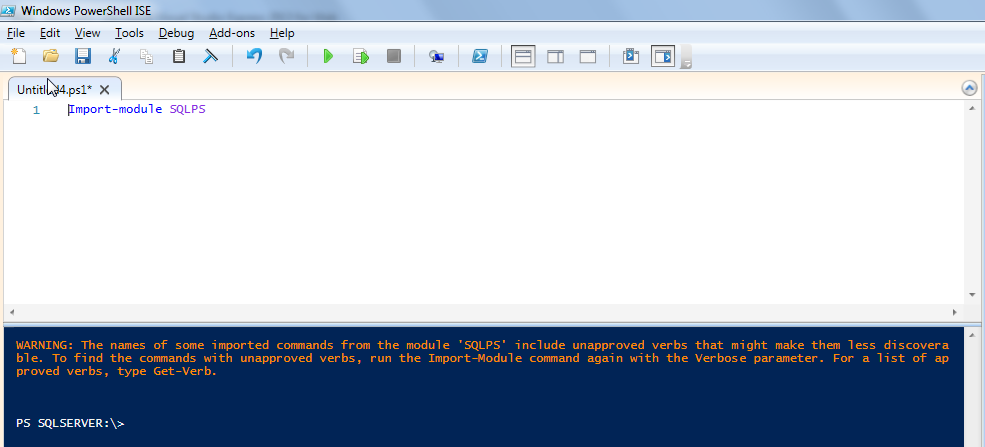
WARNING: The names of some imported commands from the module 'SQLPS' include unapproved verbs
that might make them less discoverable. To find the commands with unapproved verbs, run the
Import-Module command again with the Verbose parameter. For a list of approved verbs, type Get-Verb.
We get a message indicating that non-approved verbs exist in the module.
(Note that when you import the SQLPS module your location will be set to the root of the SQL Server provider.
This is expected behavior.)
You can avoid this error by including the -DisableNameChecking parameter to
the Import-Module cmdlet when you import the SQLPS module.
Example
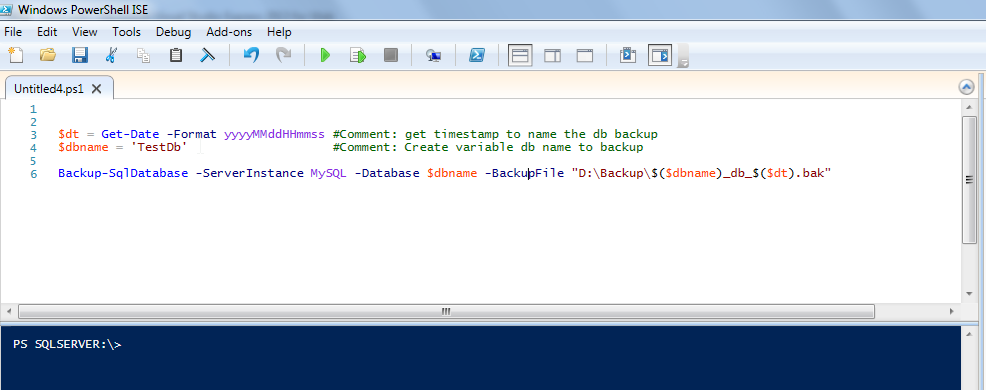
PS SQLSERVER:\> $dt = Get-Date -Format yyyyMMddHHmmss #Comment: get timestamp to name the db backup
PS SQLSERVER:\> $dbname = 'TestDb' #Comment: Create variable db name to backup
PS SQLSERVER:\> Backup-SqlDatabase -ServerInstance MySQL -Database $dbname -BackupFile
"D:\DBBackup\$($dbname)_db_$($dt).bak"
Next module we will see how to restore DB from backup file. Powershell Sql Backup Restore
Using the Command Prompt
Besides Microsoft Visual Studio and Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio,
you can use the DOS command prompt,
Like Command Prompt, you can use PowerShell to create and manage databases.
To access it, you can click Start -> (All) Programs -> Windows PowerShell 3.0 ->
Windows PowerShell. A DOS window would display:
Notice that, this time, the title bar displays SQLCMD, which indicates that the application
is ready to receive commands that relate to Microsoft SQL Server.