Welcome to this PowerShell tutorial .net, here you'll learn to make your own PowerShell scripts, If you're brand new to PowerShell then you are at right place to start learning PowerShell scripting.
Windows PowerShell is Microsoft's task automation framework, consisting of a command-line shell and associated scripting language built on top of .NET Framework. PowerShell provides full access to COM and WMI, enabling administrators to perform administrative tasks on both local and remote Windows systems.
PowerShell has power, depth and flexibility and you can research for yourself, with PowerShell you can create new objects for example, Windows Services File system , DirectoryEntry or the simpler, and .Net Framework based object using fully qualified name like system.DateTime.
PowerShell has ability to use .Net Framework and powershell allows you to build such objects.
Microsoft just kept adding more and more new PowerShell methods to make our life as easy as possible.
Output is always a .NET Object Please, Remember that PowerShell output is always a .NET object. That output could be a System.Diagnostics.Process a object or System.IO.FileInfo object or a System.String object. Basically it could be any .NET object whose assembly is loaded into PowerShell including your own .NET objects.
An Absolute Beginner's Baby steps In PowerShell you can find here.
Powershell 1.0, Powershell 2.0, Powershell 3.0
Now Powershell 5.0
What's New in Windows PowerShell 5.0 Windows PowerShell 5.0 includes significant new features that extend its use, improve its usability, and allow you to control and manage Windows-based environments more easily and comprehensively.
- Contains updates for Windows PowerShell and Windows PowerShell ISE.
- Package Management cmdlets.
- Network Switch cmdlets.
- Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC)
note: You will need .NET Framework 4.5.
Please, Have a look at the Table of contents to the left, where all the menu items are listed and be sure to come back regularly, as we will be keep adding new sections to it. We hope that this tutorial will get you started properly on Powershell.
Everything here is free, and We hope you like our work.
When you run any get command, you can see some of the properties(Not All Poperties).
It is powershell configuration which shows only configured properties cloumn.
We are coming with massive update on 'Get-Member' in Language Section..
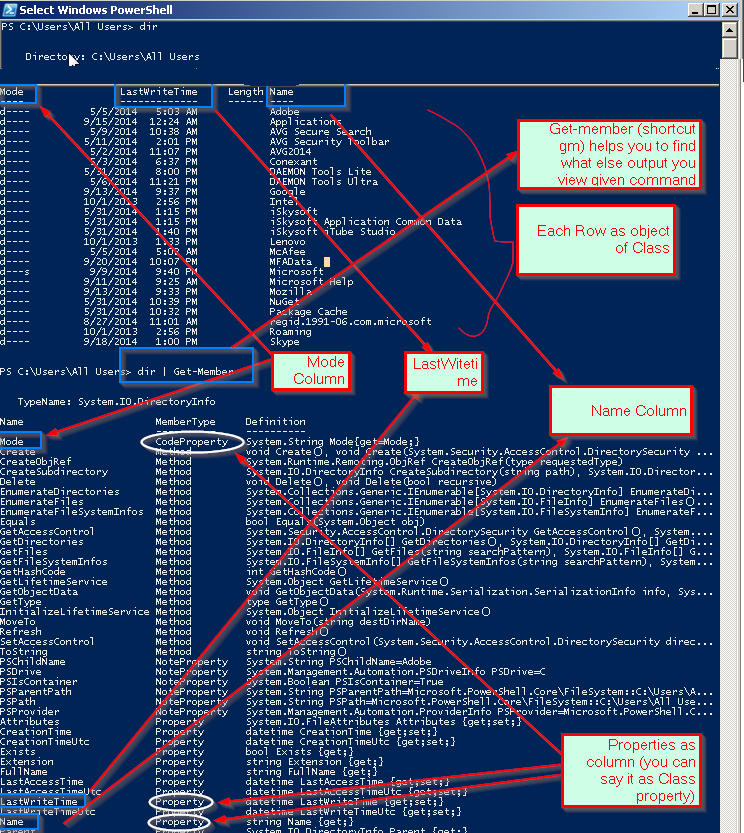
How to use powershell commands effectively one of the important to get help or find different commands.
Find commands starting with 'a'
Find commands starting with 'b' We will see one of the example where we can get the collection and query or filter or sort collection.
e.g
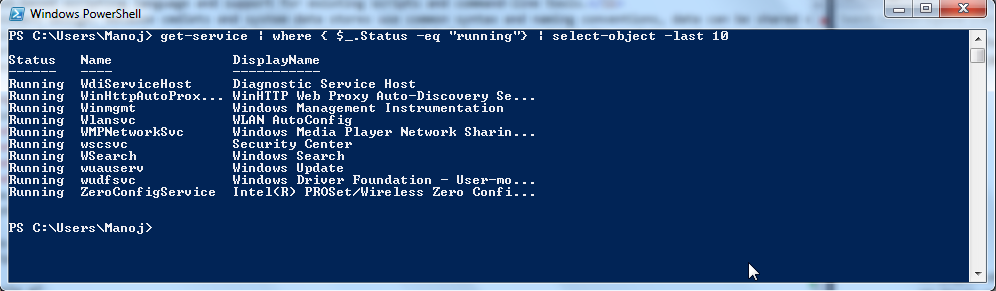
Lets consider above example "get-service" is a collection of services.
"|" use to query the collection
inside where "$_" collection variable like we have in LINQ (C#). Here query to find running services out of the collection
Finally we are taking that filtered collection (running services) taking only last 10 items (services)
Please download Powershell Essentials from below link
Powershell Essentials Powershelltutorial.pdf
RECENT UPDATES
Powershell Sleep
If you need to pause your PowerShell Script, you can add this command to your
script and force it to wait couple seconds (Milliseconds) powershell sleep read more..
- powershell Script Signing
- Powershell Sql Backup
- Powershell Sql Backup Restore
- Powershell Snapins
- Powershell Delete File
- How can i run powershell with the net 4 runtime
- How do you comment out code in powershell
- How many cmdlets Available in powershell
- How to determine what version of powershell is installed
- How to execute powershell script from c# commandline arguments
- How to load assemblies in powershell
- How to pass multiple parameters into a function in powershell
- Is it possible to create Multidimensional Arrays in Powershell
- Is it possible to run commands in parallel powershell
- What is cmdlets and its terms in powershell
- powershell Script Signing
- Powershell Sql Backup
- Powershell Sql Backup Restore
- Powershell Snapins
- Powershell Delete File
- How can i run powershell with the net 4 runtime
- How do you comment out code in powershell
- How many cmdlets Available in powershell
- How to determine what version of powershell is installed
- How to execute powershell script from c# commandline arguments
- How to load assemblies in powershell
- How to pass multiple parameters into a function in powershell
- Is it possible to create Multidimensional Arrays in Powershell
- Is it possible to run commands in parallel powershell
- What is cmdlets and its terms in powershell
- Accessing the alias drive in powershell 3
- Adding functions to the powershell ise menu
- Basic line editing tricks powershell
- Breaking down a powershell script
- Casting values in powershell
- Changing powershells look and feel
- Constant and read only variables
- Create xml variable powershell
- Creating aliases in powershell
- Creating and changing a powershell profile
- Creating persistent aliases in powershell
- Customizing-the-ise-in-powershell
- Download-file-website-powershell
- Getting-acquainted-with-the-ise
- Getting-the-right-output-in-powershell
- Getting-to-know-tab-expansion
- Growing-arrays-dynamically-in-powershell
- Handling-complex-powershell-scripts
- Hashtables-in-windows-powershell
- How-to-impersonate-someone-in-powershell
- How-to-use-powershells-invoke-wmimethod
- installing-windows-powershell-2
- query-xml-data-powershell
- Stringing-powershell-commands-together-2
- Understanding-automatic-variables-in-powershell
- Understanding-if-else-statements-in-powershell
- Understanding-powershell-commands
- Understanding-powershell-operators
- Understanding-powershell-variables-and-datatypes
- Understanding-the-windows-management-instrumentation-wmi-part-ii
- Understanding-the-windows-management-instrumentation-wmi
- Using-loops-in-powershell-part-i
- Using-loops-in-powershell-part-ii
- Using-loops-in-powershell-part-iii
- Using-loops-in-powershell-part-iv
- Using-loops-in-powershell-part-v
- Using-pipelines-to-streamline-powershell-commands
- Using-regular-expressions-in-powershell-part-i
- Using-the-switch-statement-in-powershell
- Working-binary-powershell
- Working-with-powershell-objects-via-variables
- Writing-your-first-powershell-command
- How to read a secure channel
- Managing ACLs
- Creating cmdlets in C#
- Object is a collection
- Conversion dates WMI size
- why to set up your own nuget private gallery
- PowerShell and Bing
- SSIS Deployment
- Merge and Package
- Delete Bin Obj in current folder
- load assembly from path in powershell
- How to show message box from powershell
- bypass executionPolicy
- Copy files specific extension
Windows PowerShell includes the following features:
- Cmdlets for performing common system administration tasks, such as managing the registry, services, processes, and event logs, and using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI).
- A task-based scripting language and support for existing scripts and command-line tools.
- Consistent design. Because cmdlets and system data stores use common syntax and naming conventions, data can be shared easily and the output from one cmdlet can be used as the input to another cmdlet without reformatting or manipulation.
- Simplified, command-based navigation of the operating system, which lets users navigate the registry and other data stores by using the same techniques that they use to navigate the file system.
- Powerful object manipulation capabilities. Objects can be directly manipulated or sent to other tools or databases.
- Extensible interface. Independent software vendors and enterprise developers can build custom tools and utilities to administer their software.